Wind Shear Map Pacific – Wind shear is often the most critical factor controlling hurricane formation and destruction. In general, wind shear refers to any change in wind speed or direction along a straight line. . TAFs are one way to identify the likelihood of nonconvective low-level wind shear for your departure or destination airport. [Adobe Stock] There’s no doubt that terminal aerodrome forecasts .
Wind Shear Map Pacific
Source : tropic.ssec.wisc.edu
Steady state ocean response to wind forcing in extratropical
Source : www.pmel.noaa.gov
East Pacific Deep Layer Wind Shear Latest Available Large Scale
Source : tropic.ssec.wisc.edu
Linear trends of (a) relative SST, (b) vertical wind shear, and (c
Source : www.researchgate.net
East Pacific Upper Divergence 6 Hours Previous Large Scale
Source : tropic.ssec.wisc.edu
Vertical wind shear (VWS) difference (m/s) between ENSO events and
Source : www.researchgate.net
South East Pacific Deep Layer Wind Shear 9 Hours Previous
Source : tropic.ssec.wisc.edu
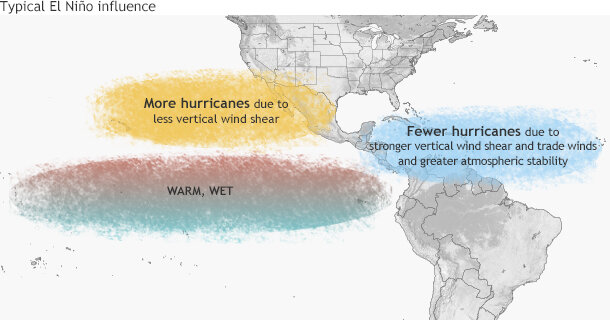
Impacts of El Niño and La Niña on the hurricane season | NOAA
Source : www.climate.gov
East Pacific Mid Level Wind Shear 3 Hours Previous Large Scale
Source : tropic.ssec.wisc.edu
Argentina 4.?height=390&
Source : sites.google.com
Wind Shear Map Pacific West Pacific Deep Layer Wind Shear 18 Hours Previous Large Scale: In the Pacific Ocean, they are known as cyclones swirling winds to concentrate the storm and a weak vertical wind shear rising from the surface of the sea. If the wind shear changes too . El Niño begins as a warming of water temperatures in the eastern tropical Pacific That addition of wind energy in the upper atmosphere induces shear, or a change of wind speed and/or .